The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a mathematical relationship that relates a person’s mass to height, developed by the Belgian politician Adolphe Quettelet and is therefore also called the Quetelet index.
BMI can also be calculated from a graph showing BMI as a function of mass and height using different categories of contour lines. BMI is a widely accepted measurement, but it is not accurate. It classifies people into underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese based solely on their weight and height. It does not take into account age, gender, body fat percentage or muscle mass. Even with the classification, there is debate today about where these limits should be placed. Generally accepted: BMI less than 18.5 kg/m2 Normal weight: 18.5 to 25 Overweight: 25 to 30 Obesity: greater than 30.2 BMI less than 20 and greater than 25 is associated with higher mortality, lower risk Between 20-25. The prevalence of overweight and obesity is highest in the Americas,
To find it is very easy, it can be achieved with a simple operation, which is the weight in kilograms divided by the square elevation of the height in meters, as seen in the image.

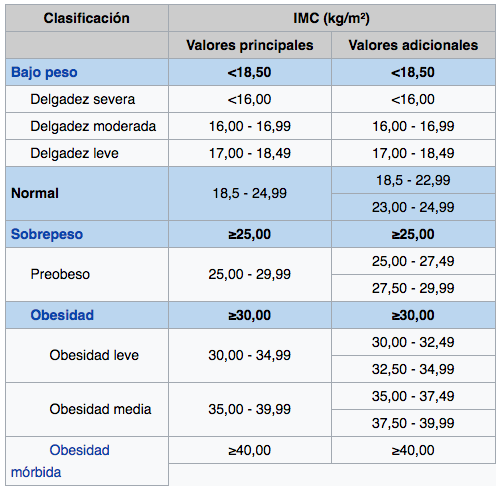
In the following table you can verify which category is:
Obesity increases the risk of diabetes and high blood pressure, the two most common causes of kidney disease. Even if a person does not have diabetes or high blood pressure, obesity itself can contribute to kidney disease and speed its progression. People who are overweight or obese can also be biased and stigmatized by others, including health care providers. This can lead to feelings of rejection, shame, or guilt, making mental health problems worse.

© Intikisa.us All rights reserved. developed by Dynamo Soluciones.
 Add Contact: +17867779201
Amount to Pay$ 0.00
Add Contact: +17867779201
Amount to Pay$ 0.00
Este método no permite hacer pagos mayores a 500 por día
Debes escanear el código QR, haz clic en «Continuar» para adjuntar la captura de pantalla (es el único comprobante de pago) y podrás completar la compra.